The Great Barrier Reef is facing a critical period of heat stress over the coming weeks following the most widespread coral bleaching the natural wonder has ever endured, scientists said Friday.
David Wachenfeld, chief scientist at the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority, the government agency that manages the coral expanse off northeast Australia, said ocean temperatures over the next month will be crucial to how the reef recovers from heat-induced bleaching.
“The forecasts … indicate that we can expect ongoing levels of thermal stress for at least the next two weeks and maybe three or four weeks,” Wachenfeld said in a weekly update on the reef’s health on Thursday.
“So this still is a critical time for the reef and it is the weather conditions over the next two to four weeks that will determine the final outcome,” he said.
Ocean temperatures across most of the reef were 0.5 to 1.5 degrees Celsius above the March average.
In parts of the marine park in the south close to shore which avoided the ravages of previous bleachings, ocean temperatures were 2 to 3 degrees Celsius above average.
The authority has received 250 reports of sightings of bleached coral due to elevated ocean temperatures during an unusually hot February.
The 345,400-square kilometer World Heritage-listed colorful coral network has been devastated by four coral bleaching events since 1998. The most deadly were the most recent, in consecutive summers in 2016 and 2017.
Scientists fear the latest coral death rate could match those events.
“At the moment, it’s definitely the most extensive bleaching event we’ve ever had,” U.S. National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration Coral Reef Watch scientist William Skirving said Friday.
“It’s certainly an end-to-end bleaching event with severe bits at each end and it’s not looking good for the southern end, but it really depends on the weather in the next two weeks,” he said.
Ove Hoegh-Guldberg, a scientist from the Australian Research Council Center for Excellence in Coral Reef Studies, said how much of the bleached coral would recover and how much would die would not be known for weeks.
“I’m very worried about the situation given how warm the temperatures are on the Great Barrier Reef and what the projections are,” Hoegh-Guldberg said.
“If it cools down a bit, they’ll recover or, if not, we may head off into something not too different from 2016 and 2017. We’re right at the fork in the road,” he added.
The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority last year downgraded its outlook for the corals’ condition from “poor” to “very poor” due to warming oceans.
Its latest report, which is updated every five years, found the greatest threat to the reef remained climate change. The other threats are associated with coastal development, land-based water runoff and human activity such as illegal fishing.
Related Stories
‹
![]()
Australians Leave Homes as Heat, Winds Escalate Fire DangerThousands of people fled their homes and helicopters dropped supplies to towns at risk of nearby wildfires as hot, windy conditions Friday threatened already fire-ravaged southeastern Australian communities. The danger is centered on New South Wales and Victoria, Australia’s most populous states, where temperatures and winds spiked after a few days of relatively benign conditions. […]
Global Climate Protests Begin Ahead of Madrid MeetingAustralians affected by recent devastating wildfires joined young environmentalists kicking off a global protest Friday demanding governments act against climate change. The “global day of action” was expected to see rallies in hundreds of cities around the world, days before officials gather Monday in Madrid for talks on the issue. Janet Reynolds in Sydney said […]
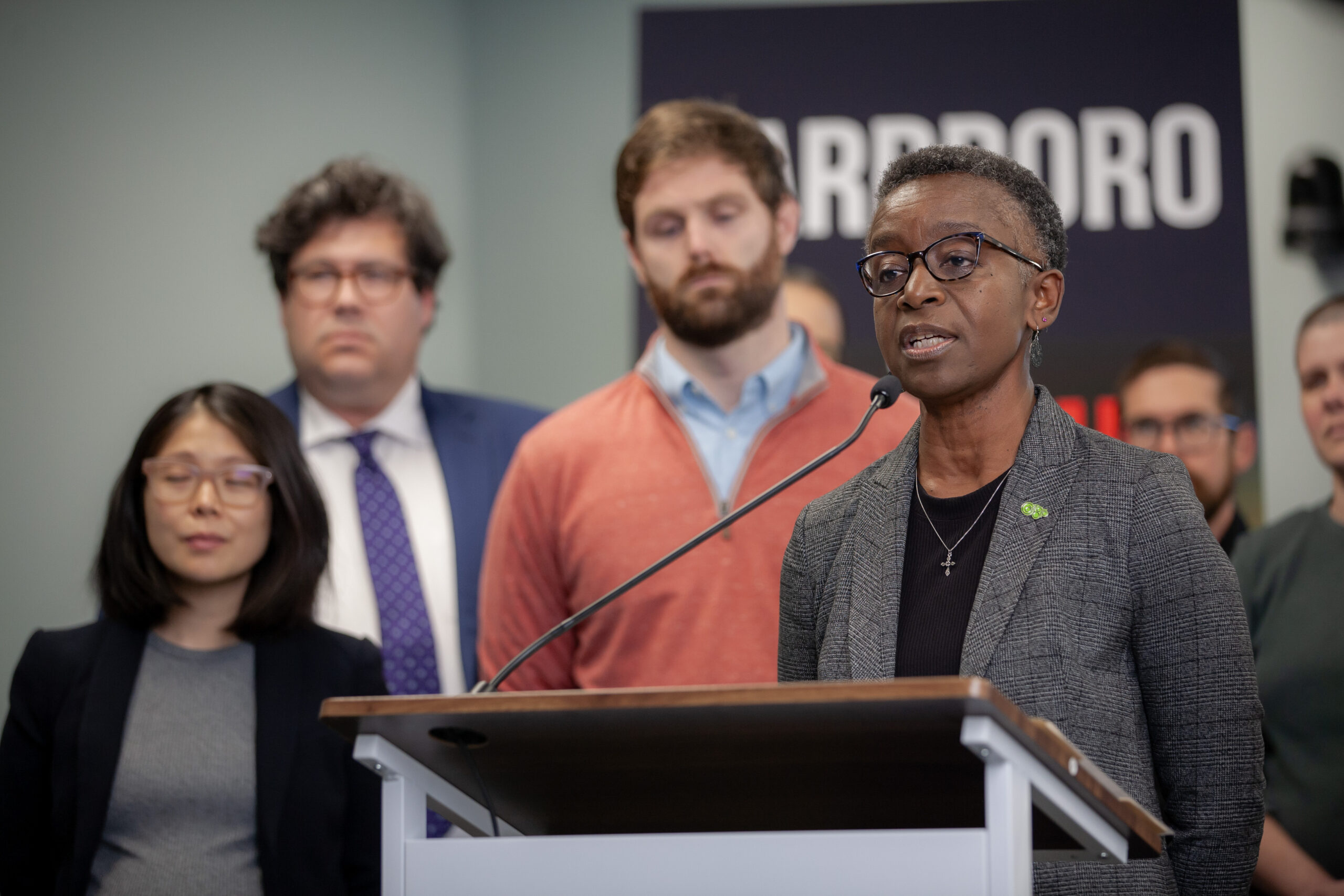

Judge Dismisses Carrboro's Climate Change 'Deception' Lawsuit vs. Duke Energy, Citing 'Imprecise' ClaimsFollowing arguments held in September, Superior Court Judge Mark Davis dismissed the Town of Carrboro lawsuit on Friday.

What If Just 1 in 10 People Changed How They Eat, Drive, Heat or Shop?Climate change is often viewed as too big an issue for individual action. But when personal choices add up, the impact can be significant.
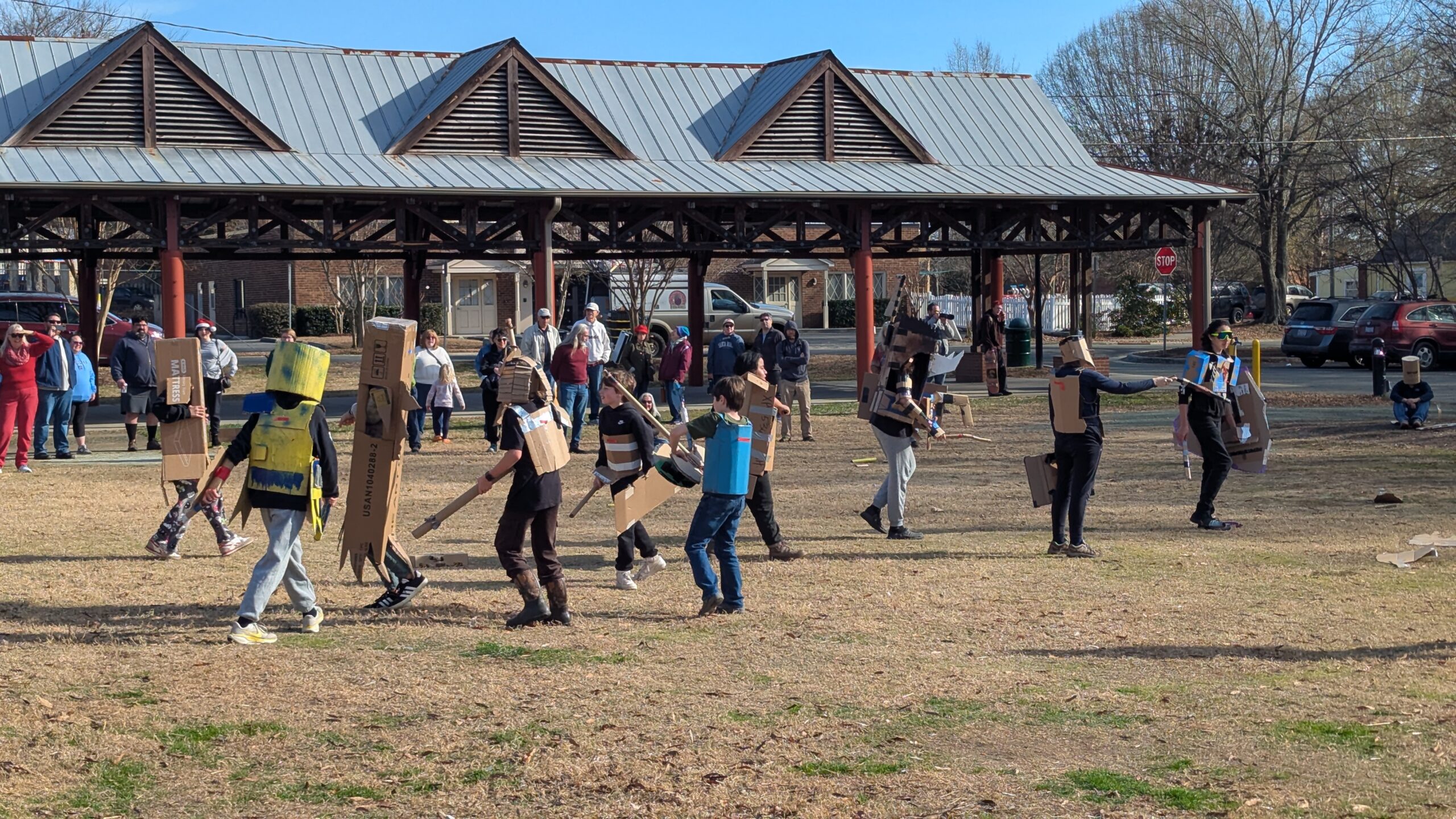

'So Much Fun': Community's First 'Cardboard War' Brings Out Creativity and WhimsyThe Carrboro Town Commons was the site of a "cardboard war" on Saturday, which was created to spur whimsy and creativity among the community.
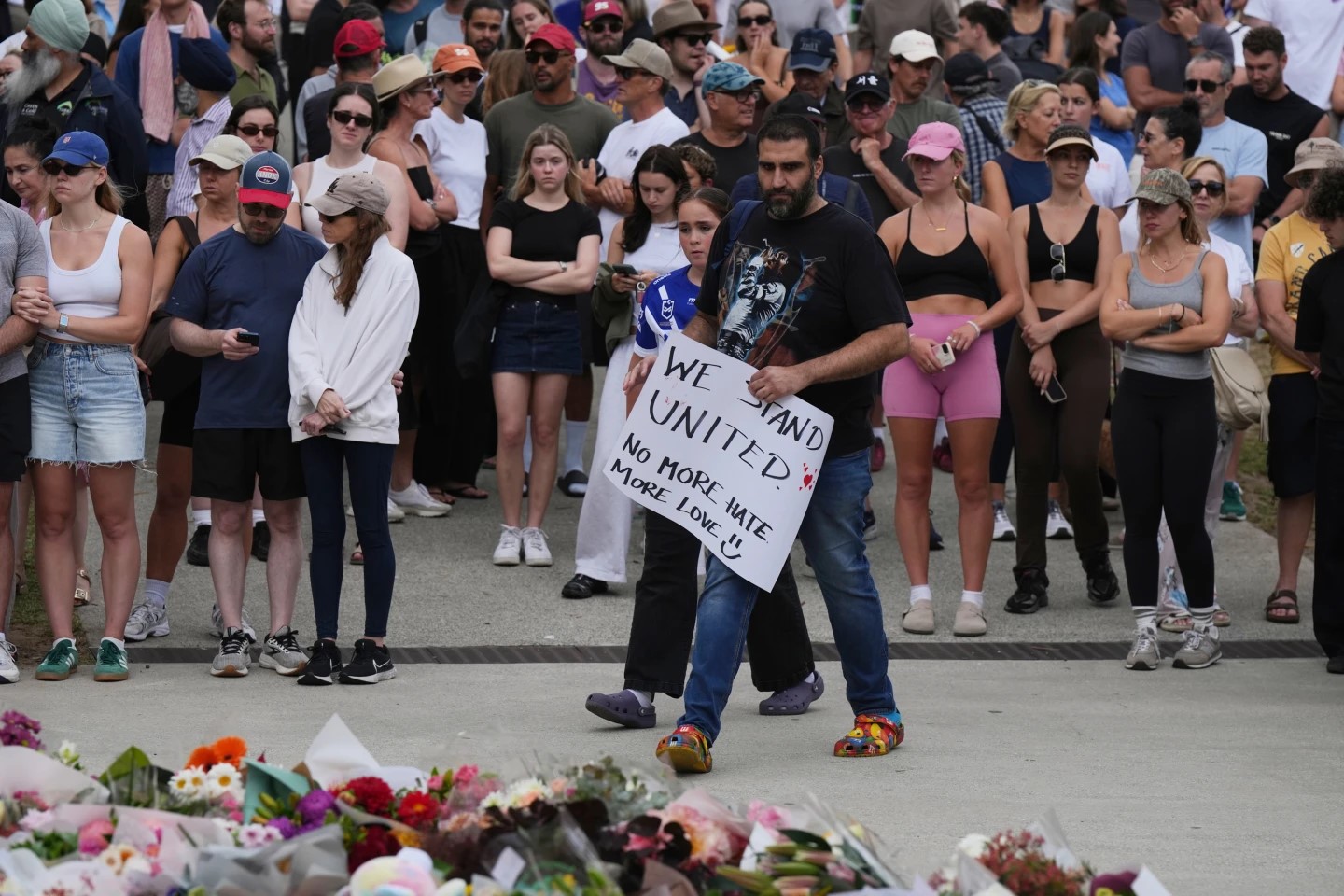

What to Know About the Attack on the Hannukah Festival in Australia That Killed 15 PeopleA father and son are suspected by officials to have killed 15 people on a popular Australian beach, shocking a country where gun violence is rare.

On the Porch: Lisa Sorg - Environmental NewsThis Week:
Lisa Sorg is the North Carolina reporter for Inside Climate News. A journalist for 30 years, Sorg covers energy, climate environment and agriculture, as well as the social justice impacts of pollution and corporate malfeasance. She has won dozens of awards for her news, public service and investigative reporting. In 2022, she received the Stokes Award from the National Press Foundation for her two-part story about the environmental damage from a former missile plant on a Black and Latinx neighborhood in Burlington. Sorg was previously an environmental investigative reporter at NC Newsline, a nonprofit media outlet based in Raleigh. She has also worked at alt-weeklies, dailies and magazines. Originally from rural Indiana, she lives in Durham, N.C.

Town of Carrboro Argues Case in Duke Energy, Climate Change Lawsuit's Initial HearingThe Town of Carrboro presented its legal rationale for continuing a 2024 climate change-focused lawsuit against Duke Energy on Thursday.
In Coastal Ghana, Female Oyster Farmers Try to Save an Old Practice Threatened by Climate ChangeIn Ghana’s coastal mangroves, oyster farming has been a key source of livelihood dominated for ages by women.

The EPA Eyes Rolling Back Rules Projected To Save $275 Billion and 30,000 Lives Every YearWhen the head of the Environmental Protection Agency announced a wide-ranging rollback of environmental regulations, he didn’t mention how ending the rules could have devastating consequences to human health.
›