Written by CARA ANNA
Africa’s rare glaciers will disappear in the next two decades because of climate change, a new report warned Tuesday amid sweeping forecasts of pain for the continent that contributes least to global warming but will suffer from it most.
The report from the World Meteorological Organization and other agencies, released ahead of the U.N. climate conference in Scotland that starts Oct. 31, is a grim reminder that Africa’s 1.3 billion people remain “extremely vulnerable” as the continent warms more, and at a faster rate, than the global average. And yet Africa’s 54 countries are responsible for less than 4% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
The new report seizes on the shrinking glaciers of Mount Kilimanjaro, Mount Kenya and the Rwenzori Mountains in Uganda as symbols of the rapid and widespread changes to come. “Their current retreat rates are higher than the global average. If this continues, it will lead to total deglaciation by the 2040s,” it says.
Massive displacement, hunger and increasing climate shocks such droughts and flooding are in the future, and yet the lack of climate data in parts of Africa “is having a major impact” on disaster warnings for millions of people, WMO Secretary-General Petteri Taalas said at Tuesday’s launch.
Estimates of the economic effects of climate change vary across the African continent, but “in sub-Saharan Africa, climate change could further lower gross domestic product by up to 3% by 2050,” Josefa Leonel Correia Sacko with the African Union Commission writes in the report. “Not only are physical conditions getting worse, but also the number of people being affected is increasing.”
By 2030, up to 118 million extremely poor people, or those living on less than $1.90 a day, “will be exposed to drought, floods and extreme heat in Africa if adequate response measures are not put in place,” Sacko adds.
Already, the U.N. has warned that the Indian Ocean island nation of Madagascar is one where “famine-like conditions have been driven by climate change.” And it says parts of South Sudan are seeing the worst flooding in almost 60 years.
Despite the threats ahead to the African continent, the voices of Africans have been less represented than richer regions at global climate meetings and among the authors of the crucial Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change scientific assessments. African participation in IPCC reports has been “extremely low,” according to Future Climate for Africa, a multi-country research program.
The costs ahead are huge. “Overall, Africa will need investments of over $3 trillion in mitigation and adaptation by 2030 to implement its (national climate plans), requiring significant, accessible and predictable inflows of conditional finance,” the WMO’s Taalas said.
“The cost of adapting to climate change in Africa will rise to $50 billion per year by 2050, even assuming the international efforts to keep global warming below 2 degrees Celsius.”
Related Stories
‹
![]()
UN: Africa, Already Suffering From Warming, Will See WorseWritten by WANJOHI KABUKURU Although Africa has contributed relatively little to the planet’s greenhouse gas emissions, the continent has suffered some of the world’s heaviest impacts of climate change, from famine to flooding. Yet from its coral reefs to its highest peaks, the reverberations of human-caused global warming will only get worse, according to a […]
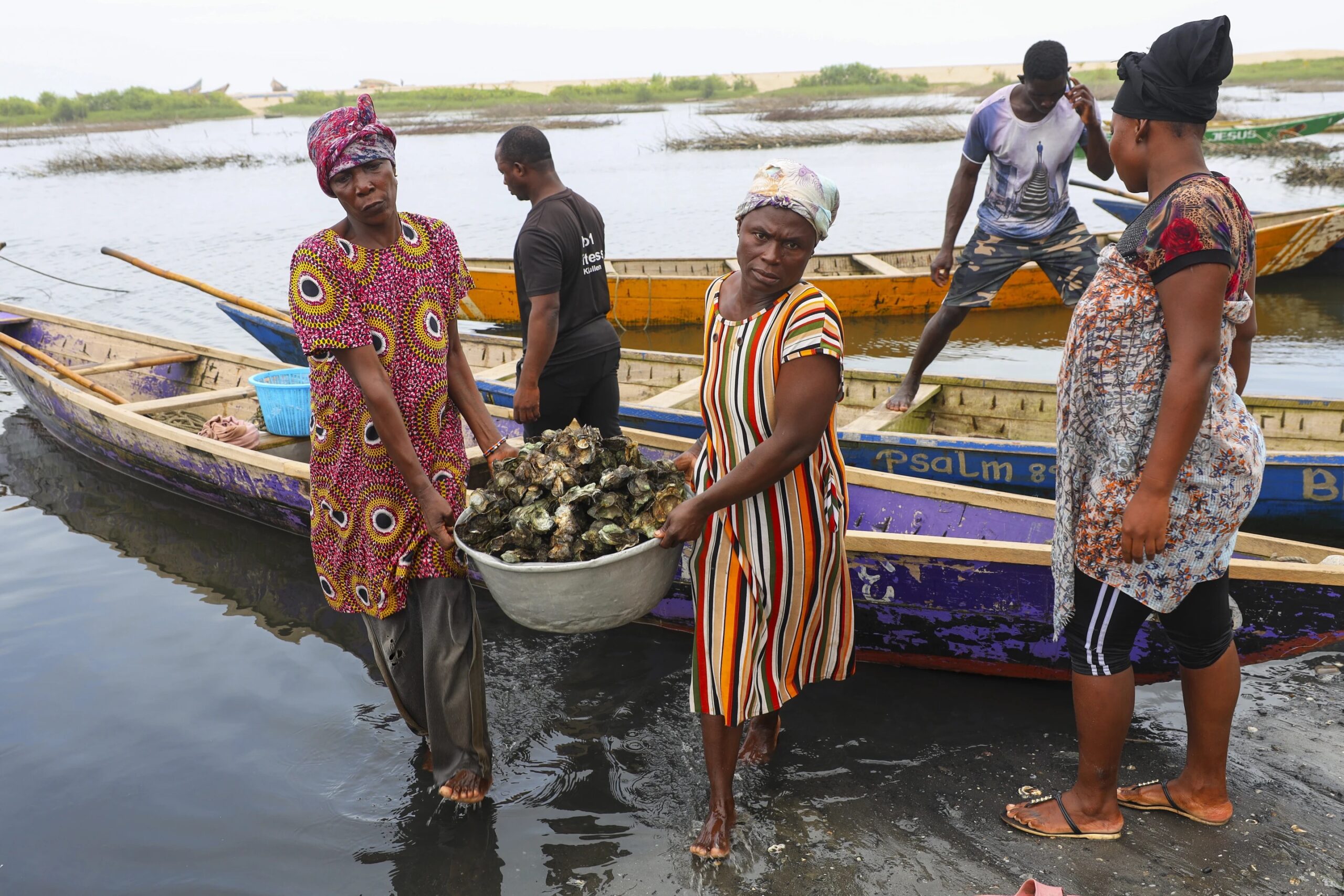
In Coastal Ghana, Female Oyster Farmers Try to Save an Old Practice Threatened by Climate ChangeIn Ghana’s coastal mangroves, oyster farming has been a key source of livelihood dominated for ages by women.

The EPA Eyes Rolling Back Rules Projected To Save $275 Billion and 30,000 Lives Every YearWhen the head of the Environmental Protection Agency announced a wide-ranging rollback of environmental regulations, he didn’t mention how ending the rules could have devastating consequences to human health.

Get Ready for Several Years of Killer Heat, Top Weather Forecasters WarnTwo of the world’s top weather agencies forecast several years of even more record-breaking heat that pushes Earth to uncomfortable extremes.

Here’s What the Paris Climate Agreement Does and Doesn’t DoThe Paris agreement is a mostly voluntary climate pact. What does it do, and what does it mean as President Donald Trump removes the U.S.?

Town of Carrboro Files Lawsuit Against Duke Energy Over Climate Change and Deception on Fossil Fuel EffectsCarrboro is suing Duke Energy over its contributions to climate change and the resulting economic pressures put onto the local government.

Athletes Speak Their Fears: Climate Change Threatens Their Sports and Their HealthWritten by DORANY PINEDA and MICHAEL PHILLIS BAKU, Azerbaijan (AP) — Pragnya Mohan has been a professional triathlete for nearly a decade, but summers in her native India are now so hot that she can’t train there anymore. She escaped the heat to train in the United Kingdom, but worries about a day when a warming world […]

How the Hot Water That Fueled Hurricane Beryl Foretells a Scary Storm SeasonWritten by SETH BORENSTEIN Hurricane Beryl’s explosive growth into an unprecedented early whopper of a storm shows the literal hot water the Atlantic and Caribbean are in right now and the kind of season ahead, experts said. Beryl smashed multiple records even before its major-hurricane-level winds approached land. The powerful storm is acting more like monsters that […]

A Big Boost for a Climate Solution: Electricity Made From the Heat of the EarthOne method of making electricity cleanly to address climate change has been quietly advancing and on Tuesday it hit a milestone.

Fewer Fish and More Algae? Scientists Seek To Understand Impacts of Historic Lack of Great Lakes IceWritten by TODD RICHMOND Michigan Tech University biologists have been observing a remote Lake Superior island’s fragile wolf population every winter since 1958, but they had to cut this season’s planned seven-week survey short after just two weeks. The ski plane they study the wolves from uses the frozen lake as a landing strip because […]
›